so now iwonder how morning im bolus , would compare to sub q bolus ??
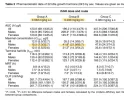
I've spent hours looking at every angle of this, running it through simulations, comparing to the very few studies using healthy subjects, and, of course, it's complicated.
The takeaway I've come up with is that from the GH receptor mediated effect perspective, like fat loss. skin / tissue repair, immune system boost, cognitive / mood boost, for all intents and purposes an IM dose acts like 2x the same dose subQ.
It acts like slightly less than the subQ dose for IGF mediated effects like anabolic muscle mass increase and repair.
So 4iu IM would look like the equivalent of SubQ:
8iu: GH effects
3.6iu: IGF effects
Sides would be similar to 8iu subQ, since rHGH sides are caused mostly by GH.
While I'm sure there are many more
nuances this is probably the most significant: lipolysis in healthy young men seems to max out around 3iu. With age, insulin resistance, fibrosis, and other damage "stubborn fat" requires more GH to release FFAs. 5iu+.
Lipolysis won't double because it'll max out first, but other effects aren't capped like skin / tissue repair.
If the primary goal is muscle mass / repair, subQ would be a little more efficient at boosting IGF exposure (at the same dose as IM). You could increase the IM dose 10% to compensate.
The 10% IM IGF AUC (total exposure) loss may be because the much higher GH spike causes receptors on the liver to downregulate making IGF conversion less efficient. But it's more important we know that it happens, from the Keller clinical study, than why it happens,
It still looks like IM is all upside unless you need to squeeze every drop of anabolism out of a dose, or get intolerable sides from the higher GH exposure. Except that it's a daily IM injection.... 30g 1/2" is easy though.
Unfortunately no long term studies on clinical outcomes using IM vs SubQ to confirm all this. The ones that come close focus on IGF levels and growth in short stature children, and they're similar with both.